The consequences of spray foam
Carbon dioxide emissions are proven to be the main cause of global warming: eighteen of the nineteen warmest years on record have occurred since 2001. Buildings account for 8.67 GtCO2 of the annual global emissions of 32.84 GtCO2, making the building industry one of the greatest single contributors of emissons worldwide.
Spray foam has been available since 1986 and has become extremely popular in the building sector due to its energy efficiency. This material can act as both an air and vapour barrier, limiting the amount of air and moisture that flow through assemblies. Many companies advertise spray foam insulation as a “green” building material because it offers a high R-value, thus reducing the energy bills, and is a durable material. However, there are 3 main negative consequences to using spray foam:
Health Risks
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that are released by spray foam can cause asthma and other lung irritations. Houses are required to be vented for up to 24 hours after installation, and off-gassing continues in lower amounts thereafter.
Need for Expert Installers
Expert installers are required to properly mix the foam compounds together to avoid failure of the material. The main concern is that spray foam can shrink and separate from the structure, eliminating the vapour and air barrier system that the material is meant to create. Spray foam is also highly flammable.
Environmental Risks
Spray foam contains many blowing agents that have extremely high global warming potentials. Chemicals such as HFC-245fa are commonly used and are up to 1000 times worse for the environment than carbon dioxide.
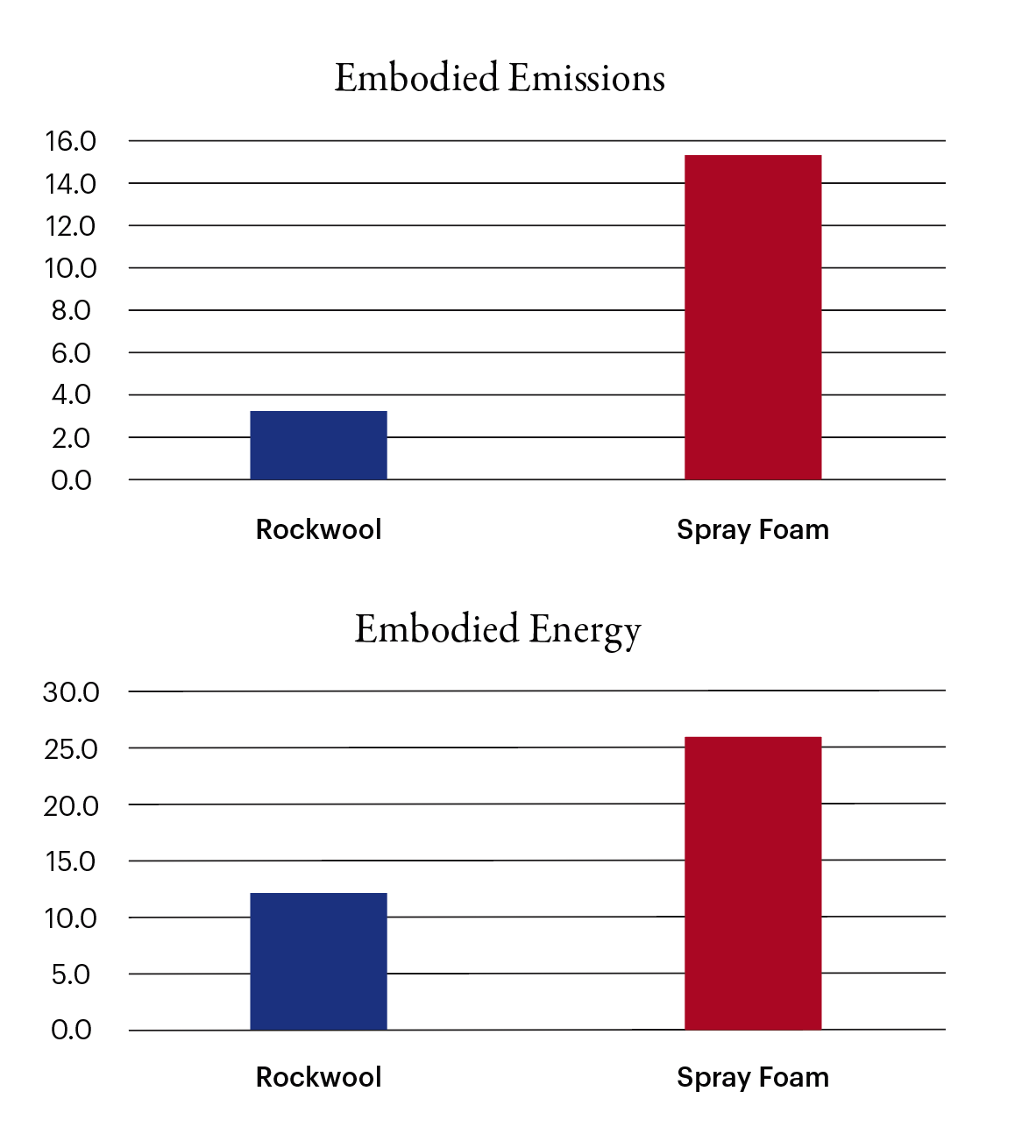
At Sustainable, Rockwool is preferred over spray foam because it has a lower embodied energy and fewer emissions when manufactured. Additionally, Rockwool is easy to install and does not contain VOCs.
Sources
1 - https://climate.nasa.gov/
2 - https://www.iega.org/statistics/co2emissions/
3 - https://www.cbc.ca/marketplace/m_blog/is-spray-foam-safe
4 - https://www.epa.gov/saferchoice/potential-chemical-exposures-spray-polyurethane-foam#curing-rates
5 - https://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/nova-scotia/do-it-yourself-spray-foam-insulation-dangers-1.4684202
6 - https://www.energyvanguard.com/blog/foam-insulation-global-warming-potential-and-bs